Engineering Capstone Proposal Denis Ryan 97055507
Table of Contents
Document Control 3
Capstone Project Proposal 4
Problem Posing and identification. 4
Background 4
Project Outline 4
Technical Summary 5
Why an Emotion Detector? 7
Assumptions 8
Relevant Literature 8
Key Technical Assumptions 8
Non – Technical Assumptions 8
Verification of Assumptions 8
Evaluation 10
Project Outcome 10
Project Process 10
Strategies and Resources 12
Software Requirements: 12
Equipment and Laboratory Requirements: 12
Data 12
Time line and contingency Plan 12
Time line and Key milestones 12
Risk management 13
Context Establishment 13
Goals 13
Risk Identification 14
Risk analysis. 15
Risk Evaluation 17
Risk Mitigation 17
Monitoring and review 18
Communication and Consultation 18
Literature Review 19
APPENDIX A – Project Timeline 20


|
Document Version |
Date and Author |
Comment |
|---|---|---|
|
Vers 0.00 |
3-8-2003 Denis Ryan |
Draft Release |
|
Version 1.00 |
6-8-2003 Denis Ryan |
Final Release |
|
Version 1.01 |
11-8-2003 Denis Ryan |
Errors corrected |
|
Version 2.00 |
12-9-2003 Denis Ryan |
Updated Version |
|
|
|
|
Electronic computing has been a part of industrial, technical and social culture for over 60 years. Computers assist the human species in solving problems, increasing productivity and help manage complexity.
Throughout the last 60 years of computing development, engineering energy has been spent in making computers more accessible to a broader spectrum of people. Human - machine interface is fundamentally difficult as the two entities are both complex and very different in design and nature.
Humans are complex emotive biological organisms that process input via sensory processing regions in the temporal regions of the brain. Processing is based on interpretation of whats seen , heard, felt or smelt. Many of these inputs are coloured by associations and emotional states. On the other hand computers, while a complex entity, have rigid and well defined means of accepting and delivering information.
Human – Machine interface has developed extensively, with information delivered originally by switches and load buttons then punch cards, keyboards, pointing devices and more recently via speech recognition.
The latest technology of speech recognition provides a natural form of human machine interface. At last machines are able to interpret information contained in the words that are spoken at them, however they still cannot interpret other (possibly vital) information that is delivered with the spoken input. This other information may be emotional data representing, urgency, anger, confusion or elation. In many cases this input may be more important than actual words spoken .
There is a number of ways we can detect a person's emotional state. Every day we as human beings assess the emotional state of other humans when we interact with them. At a conversational level whether its face to face or over the phone we can “listen” to emotion in there speech.. How many times do we comment: - “You're amazingly chirpy today”, “you sound stressed” or “Is something wrong – you sound so glum”? We do not need to interact face to face with the person to analyst these states – over the telephone one can detect emotion simply by the level and intonation of the voice.
The chosen vocabulary also is a strong indicator of emotional alignment. An angry person may curse or use obscene language while an elated person may repeat words such as “great”, “fabulous” or “wonderful”. Everyday words we use can indicate many things depending on their context.
The project I have chosen to undertake for my engineering capstone is based on the development of a computer based system, designed to interpret human emotion via the spoken word. There has already been quite a lot of research in this area being conducted by individuals and specific organizations alike. The aim is to develop an economically viable system that can reliably interpret emotional state through voice, for the broadest spectrum of human users as possible.
The project will be conducted in multiple stages. The first part of the project involves a considerable amount of research into the physical and physiological aspects of human speech and the influence of emotions. Next a simulation will be created which will process recorded .wav files to produce a reliable result based on the emotional quality of the speech recorded. The simulation will employ specific Speech analysis software such as “PRAAT” or the “COLEA” toolbox in Matlab or both. For stage three I will interface as real-time version of the simulation an IVR system which can be accessed via the PSTN. The IVR will provide instant feedback on the audio channel using a number of different demonstrations. To complement the live demonstration a Java based console will be devised enabling the “setup” of the systems behavior. The final stage involves the transfer of the system to a TI DSP development platform, providing an embedded version of the technology..
Emotional content of speech can be analyzed on two levels. Low level analysis is accomplished by filtering speech into constituent components and applying logic to decide on emotional state. A higher level analysis can be achieve using a speech recognizer to filter out particular words such as swear words, loud noises or words used out of context.
The project will use a two stage detection system will will consist of a speech recognition based filter, referred to as “speech recognizer” form this point on, for the 1st stage and an speech analysing filter as the final stage. What the speech recognizer does not pick up, the speech analyser may.
The construction of the filter involves simultaneously presenting the utterance to both the speech and energy recognizers. Each recognizer analysis the input and produces either a true or false output or a fractional value between 0 and 1 known as a confidence level. Ideally the binary output from each recognizer are logically ORed together so if a true result is produced by either or both recognizers, a true result would be produced.
In its most fundamental functionality the system will be able to detect negative emotions, namely anger, within speech. In the case of this project the recognizer returns a “true” when a negative emotion is detected. The system can also also be configured to detect a number of emotions such as happiness or sadness.
The speech recognizer will employed will be most probably IBM's “Via Voice” which is a Speaker Independent Recogniser (SIR) and as it is available for Linux based platforms. Detection is used only for a small subset of words (for example swearwords). Under these conditions Speaker Independent recognizers work exceptionally well. A template of chosen words will be set for the recognizer with a cross section of accents representing the cultural distribution of Sydney Australia.
In order to achieve reliable emotion detection through speech DSP based detectors must be designed to analyze fundamental speech patterns. Th composite of these speech characteristics make it possible for a computing system to detect emotion. Four specific speech qualities can be analyzed to achieve this.
Pitch
Energy
Duration
Formant – Any of several Frequency regions of intensity in the sound spectrum which determines the characteristic qualities of sound.
On top of these features voice qualities such as rhythm, pausing and jitter will be used to further enhance the system's performance.
This project will concentrate mainly on energy levels, pitch and duration to decipher emotional state. DSP Digital Filtering will be used to break down utterances into these key characteristics which are compared to stored templates. Results from this pattern matching operation are analyzed and inserted into an “Emotion Matrix”, resulting in the derived emotion associated with the utterance. The Emotion Matrix is the key mechanism in this project and will lend itself to different levels of complexity varying from simple preset vectors to Artificially Intelligent self learning systems. For this project this engine will remain fundamental so most energy can be expended in the reliability and accuracy of the system.
In essence, an affective computer would utilize the “Emotion Matrix” onto which the emotions are plotted against all the speech characteristics. There are a number of ways of constructing such a model.
The speech recogniser function will initially be simulated with Matlab functions or PRAAT Script which will process supplied audio files, analyse characteristics through a suitable digital filter simulation and generate an result that corresponds to the emotion detected in the audio.
At an abstract level emotion in speech can be categorized into two levels, negative and non negative emotions. Negative emotions include anger, frustration and despair while non-negative emotion includes, happiness, neutrality and delight. The separation of speech into these two emotional categories, while lacking the fidelity of full emotion analysis , will provide import information to any system processing spoken input. For example non-negative speakers may be well left alone while negative speakers may qualify for external assistance or support.
The Emotion Detection project is categorized as “Experimental Investigation” under the Capstone Project categories. The project correlation of material already published from other research conducted as well as personal research and development and running of speech based experiments. The project explores new technology which is a little left field of normal DSP technology. It requires an understanding of speech and the human psych.
I elected to pursue this project as it lies close to my experience in design and creation of Interactive Voice Response and Speech Recognition projects. Experienced gathered from fine tuning such systems to deliver premium accuracy hopefully will translate into the successful evolution of the Emotion Detector project.
It is assumed that there is enough literature on the subject to give an underlying foundation to the creation of the Emotion Detection System. It is also assumed that there is some type of open consortium for information exchange related to this technology. Many honours and PhD thesis have already explored this technology.
Key technical assumptions include the software and hardware to be used for the project development. It is assumed that my personal copies of the software required are still functional with the fall back of using the universities facilities if by chance something does go wrong with my home equipment. This is also directly applicable to hardware required. Other assumptions include the availability of technical resources and expertise if and when required.
Non technical assumptions are based around the demographic that may be involved in the demonstration of the system. My aim is to verify that the system will work over a large cultural cross-section as possible. Emotions vary from culture to culture. Some cultures demonstrate a high degree of sarcasm. Some cultures have a spoken language to may sound abrupt and aggressive to members of other cultures ( eg German as compared to French). The major assumption here is that the system will be demonstrated on an English speaking Australian audience.
By the time this proposal has been submitted, all software and hardware requirements, apart from the TI 6000 development platform, will be tested for operation. The computer network at home is composed of three identical servers connected via a 100Mbit router. Each machine has a removable drive for backup.
The Ti 6000 development board is not required until mid October. Reservation of this device for the project will be organized through my supervisor. It may prove beneficial if I personally buy a development kit to avoid any conflict with other projects occurring at the same time. I will discuss this with the supervisor.
Availability of documentation is still yet to be fully verified. There is ample research being conducted in this area so it is safe to assume that technical literature will be available.
Technical support will come from both A Kadi my supervisor as well as one or two speech companies which have personal friends in their employ.
The demographic involved in testing the technology will be English speaking Sydney residents. Although accents vary widely, emotional traits when speaking English tend to follow a fairly standard pattern.
To determine the success of the project the desired outcomes need to be clearly defined and stated in a non technical manner. The project has many facets each contributing to the overall outcome and success of the project.
The desired outcomes for the Capstone project include:-
Capstone Document professionally
presented that is accurate, informative and
interesting.
Communication is a fundamental aspect of
engineering. Well structured and accurate documentation is
paramount to any engineering project.
Emotion Detection successfully
simulated in a Matlab or other environment.
Modeling is also
another highly important facet of engineering. An engineer needs
to be able to model physical entities using a variety of tools at
his or her disposal. Modeling can help decide the viability of a
project and help predict any complications that may incur time or
financial penalties during the course of development.
Emotion Detection successfully
ported onto a Ti 6000 series development platform
The
penultimate engineering goal is the finished product. The project
is 'delivered' once it exists in its intended environment. In the
case of the emotion detector the intended environment is phone or IP
based audio conversation, conferencing or computer input.
Telephony access via IVR route for
demonstration purposes.
Demonstration of an engineering
technology is a critical part of communication. People require
“look and feel” interaction with any product to help
them pass there own judgment on its viability. The IVR route will
allow people to call and trial the technology using any telephone.
Successful Presentation and
demonstration of the technology.
Finally Presentation of an
technology or idea remains an important engineering aspect. This
may not be a vital engineering quality, but can be of major benefit
when trying to send a message to the minds and hearts of
stakeholders.
Key items and events that signify the success of the project's process include:-
A well maintained and succinct
journal.
A running journal is an essential part of any
ongoing engineering project. It is a collection of events that log
each aspect of the project's development. It enables the engineer
to backtrack and refer to issues encountered at any point during the
project's evolution. It also serves as a diary of appointments and
events and is an invaluable summery of the progress to date.
Regular liaison with supervisor.
Communication with the client is
another quintessential aspect of engineering. Weekly meetings and
consultations plus prototyping all serve to give the client comfort
in the fact that the project is progressing. Even if problems are
encountered to client needs to be informed of the status to ensure
confidence is upheld. In the case of the capstone project, the
supervisor is the customer representative who needs constant
feedback on the project's progress.
A good report from supervisor on
project development.
Client satisfaction is represented by
the supervisor's assessment of the student's engineering prowess.
How well the project is progressing, how organized is the student
and how well he/she communicates will all be assessed as part of the
project's overall assessment.
Meeting milestone dates in
accordance with project time planner.
Planning is a an
important but difficult facet of engineering development. Being
able to estimate work time, possible hurdles and other unforeseen
events comes from careful planning techniques, experience and
intuition. A student engineer generally does not enjoy the luxury
of experience so has to plan carefully. Also consultation with
other engineers or even knowledge bases can prove to be
advantageous. Hitting milestones is very difficult but as long as
contingency is properly managed the project can progress with out
major breakdown.
Adherence to AS/NZ 4360:1999 risk
management standards.
The Australian Risk Management standard
is an ideal base to manage any engineering project. It is a guide
for the engineer that prepares him for the project at the initial
stages by scoping the project and putting it into context. Risk
management ties directly with project management with the two
disciplines being closely interrelated.
Two key software products required for the project are Matlab and the TI eXpress DSP development environment required for the Ti 6000 DP development unit. Other software tools that are required are Open Office Word Processing and Maths Calc Spreadsheet. Most Development will be performed in a Linux OS environment with VMWare accommodating Matlab and the Ti DSP software which are designed for a Microsoft environment. For the speech recognition engine a simplistic word based engine such as IBM's via word may be utilized.
Primarily the DSP Lab on the 23rd floor will be the main requirement. This will only be required in case of failure of home based equipment. (See Risk Management Below)
Data required in the form of utterances that have been digitally recorded in accordance with particular characteristics. For example speech that bears strong characteristics pertaining to particular emotions that will aid development and verification of the project. Speechworks Pty Ltd Based in Sydney have data of this type for my disposal.
Data will also be collected by the use of voice based interactive services prompting experiment participators to express utterances with certain emotions.
Other data required pertains to the construction of speech templates for the word recognizer.
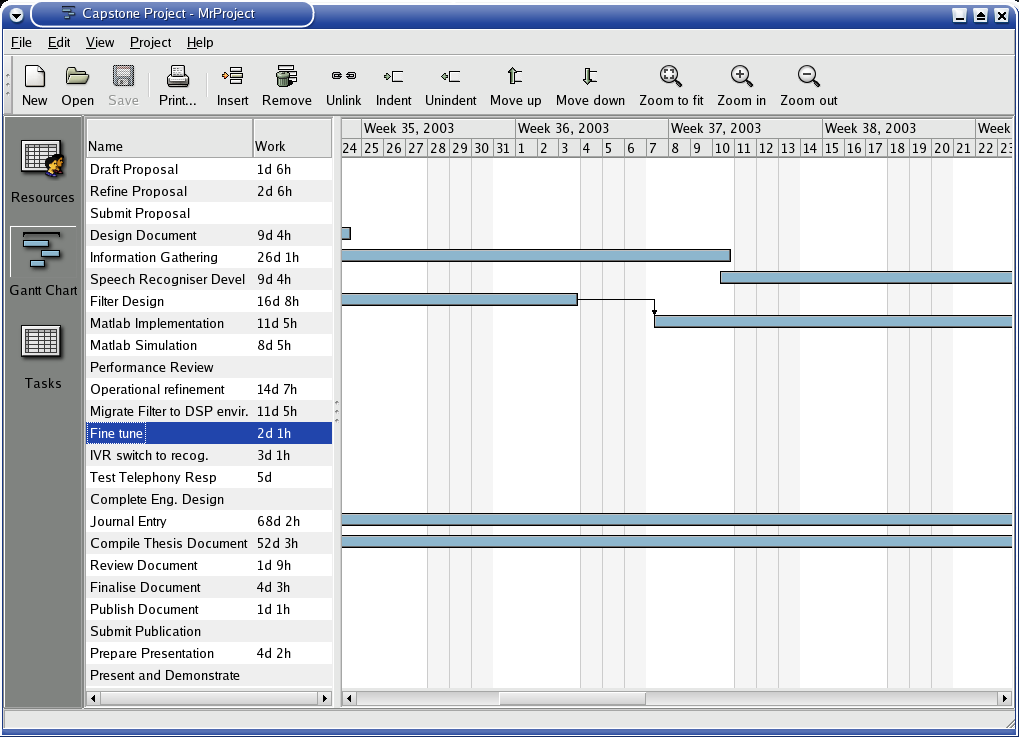
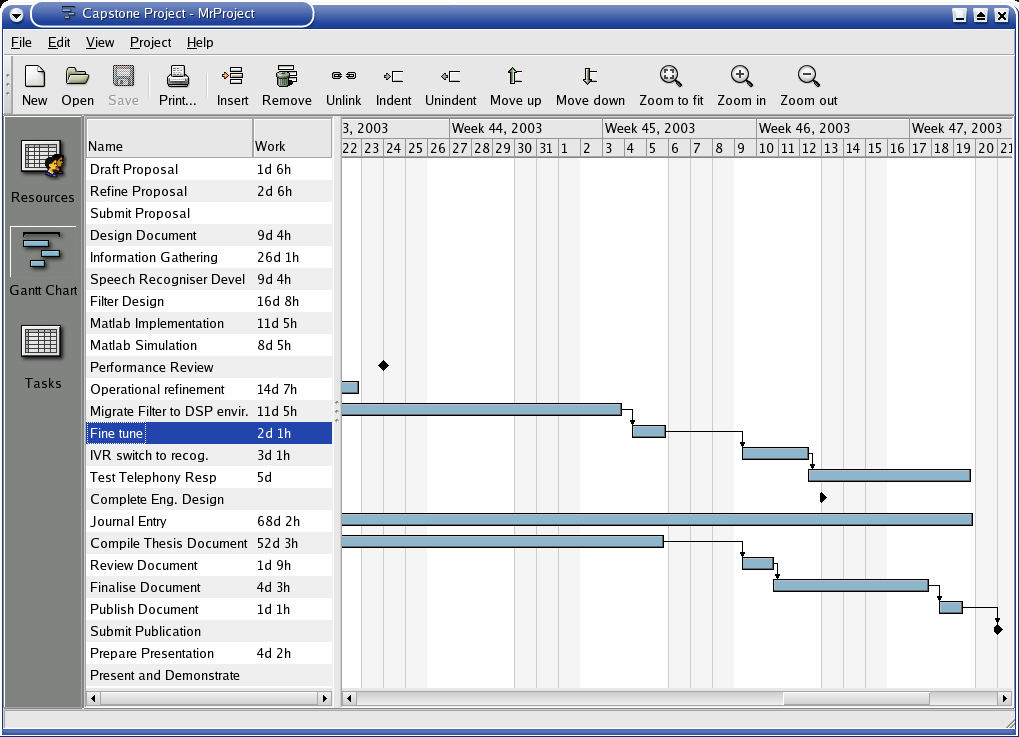
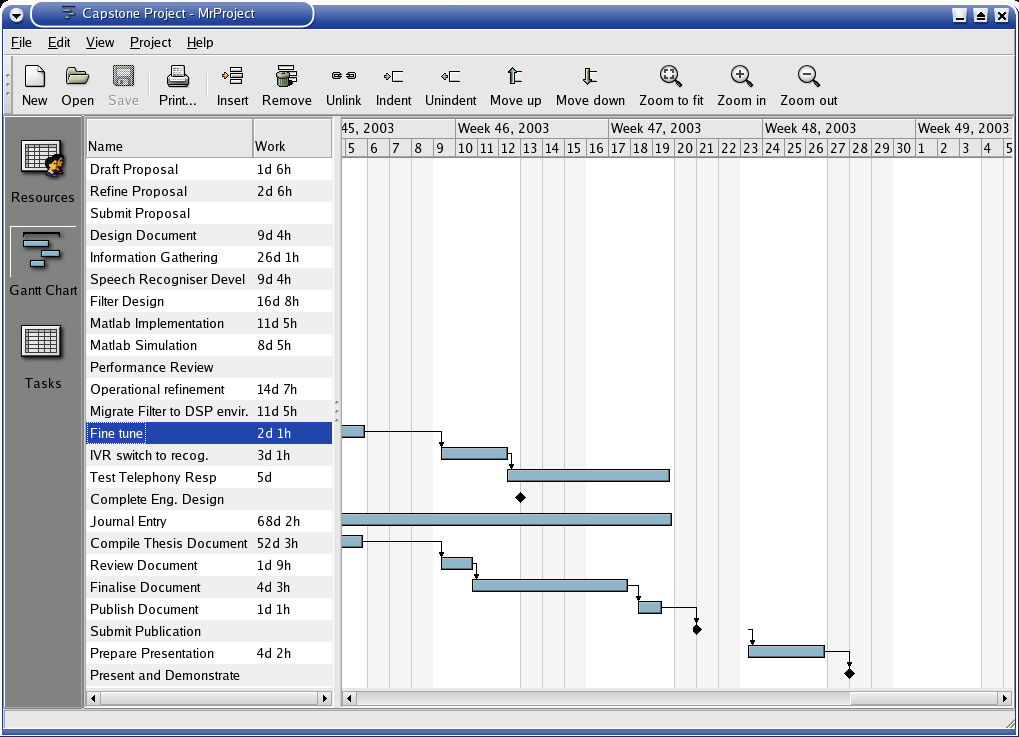
The Time line attached in Appendix A will illustrate the time allotments to the various components of the projects including the various milestones. These milestones are an indicator of the project's progress and indicate the likelihood of successful closure. The contingency plan is dealt with in the Risk Management section below.
See Appendix A attached.
The AS/NZ 4360:1999 Risk management standards will be used for this project.
Contextually this project is experimental research conducted by a lone researcher who will use his engineering prowess to research and investigate a technology that is technically in its infant stages. The researcher student engineer is of reasonable intellect is of mature age and has fair access to data and documentation from one or more voice engineering companies. The researcher has had 20 years experience of both analytical problem solving and programming/ scripting.
It is imperative that the researcher successfully fulfills the requirements by the drop dead date so he is able to graduate next year. It is highly preferable that he produces an outstanding result to improve his changes of receiving an honors degree. The researcher has reduced his work hours to 15 hours per week in order to achieve the best possible result for the project.
Stakeholders in the project include the UTS collaboration research facility as well as the student researcher. The emotion detector will play an important part in the UTS telecommunication collaboration project. UTS as a stakeholder would not bank on a guaranteed result, as work by students cannot always be guaranteed. However to the student researcher failure will cause direct interruption to his lifestyle plans for the next year.
The prime objective is to research and develop a reliable technology that deciphers emotions in speech within the designated time period. The minimum requirement is to differentiate between negative and non-negative emotional states with a superlative goal of detecting four different emotions in speech.
Anger
Despair
Elation
Neutrality.
A further achievement would involve the adaptation off the mathematical test model to a test DSP system directly processing voice through a micro phone or telephone input. The final goal is to provide an interesting, accurate and informative Capstone document which will provide a sound base for continued research in this area.
The are a number of risks invoked with the undertaking of this type of project where the time frame is relatively short and the subject matter is rather leading edge.
Insufficient literature to support recognition
algorithms.
Current research may prove to be abstract with no
real in depth modeling of emotion detection.
Insufficient support from 3rd party corporations
possessing speech data.
A degree of the research into the
project will be based on data gathered by certain corporations that
have had some investigation in this field. Data is in the form of
utterances recorded in various emotional states coupled with
information pertaining to audio characteristics to be analyzed. A
firm contact has not yet been made to secure delivery of data
required. This is not a show stopper as there is quite a bit of
sample data on the web. However it would be of major convenience to
receive experimental data from the corporation proposed.
Overly complex DSP filtering exceeds researcher's programming
ability.
Possible underestimation of programming complexity
involved with DSP filtering both with Matlab simulation and /or Ti
C60 DSP. This may be due to improper estimation of programming time
required when drafting the project time table.
Emotion Detector complexity too high thwarting attempts to
allow reliable recognition.
This is a fundamental situation
occurring when all other aspects of the plan go accordingly except
for unexplainable reasons the project does not perform to the
expected degree as agreed in the initial contract.
Hardware failure.
Major hardware failure on
development computer causing irreplaceable document or information
loss may severely hinder or even totally thwart project success.
Also applicable when transferring the project from the
Matlab simulation to the physical DSP filter. It is possible to
cause damage to the Ti development board which may incur a financial
penalty if excessive failures occur.
Personal injury or other personal problems.
Personal
trauma or tragedy such as a car accident or death in the family may
prevent successful completion of the project in the required time
frame. Other personal disasters include theft or destruction of
development equipment and / or documentation.
Insufficient literature.
Research in the area of
emotion recognition or detection has been ongoing for nearly 10
years. There is more than enough literature available pertaining to
the construction of speech based on emotion. Actors are taught how
to express emotion in there voice by following certain guidelines
which are based on quality and tone of their voice. Much of this
information has been acquired by researchers into emotion
recognition. There is a plethora of this type of data available on
the Internet as well as scores of publications available in
Australia.
Unfortunately the is not as much published
literature pertaining to the mechanics of emotion recognition using
digital filtering systems. I have managed to secure some useful
information, however much of this is quite high level.
The
finished product may be a simple anger detection system or may have
finer resolution being able to differentiate between a number of
different emotions. A demonstration of emotion detection should be
ample for this project.
The consequence of this is that I
still will be able to produce a informative research document but
will be unable to physically demonstrate the full resolution of the
system.
Risk Factor: Moderate
Consequences: Low to Medium
Insufficient Support
Speechworks Pty Ltd have had
involvement with emotion detection research by supplying speech
data. Speechworks (formally known as Altech) are the foremost
developer of speech recognition technology in the global arena. I
know key people in the Australian organization including the CEO,
who may be able to assist me in procuring speech data. This data
would be exceptionally useful but is not a show stopper. I have
sourced a fair bit of emotion speech data from the Internet.
However possible support from Speechworks personnel would also be of
great advantage.
Risk Factor: Moderate
Consequences: Major Inconvenience Only.
Programming Too Complex
Digital Filtering programming
whether it is on a Matlab simulation or straight on the DSP
development system, can be difficult. In analogue systems Filtering
tends to be an art as well as a science. This to a degree
translates to the digital arena. Experienced DSP filter designers
can work miracles , however my experience is rather limited. This
is not of a major concern as I have a high degree of confidence in
my ability to program and I have a reasonable handle on Matlab.
Translating algorithms into Matlab/ DSP code will prove to be
challenging but feasible. Failure to deliver product manifested as
a demonstration platform may not qualify capstone award.
Risk Factor: Low
Consequences: Severe
Project performs at a lower level than expectations
The situation may arise where the Emotion Detector does not
perform up to the agreed level. For instance the system only
detects anger 50% of the time instead of an agreed value of 90% of
the time. It may have a high level of inflexibility where it
responds only to a narrow spectrum of human voice.
Many
leading edge technologies suffer from such problems. Until very
recently speaker Independent Speech recognition suffered greatly
from broad accents or people speaking at too fast a rate. Much of
the technology in the latest generation speech rec engines is used
to overcome such inflexibility. In terms of the infant emotion
detector technology it is to expected that the system will not work
perfectly or even very well. It is a fundamental system that
demonstrates “promise” for such technologies.
Risk Factor: Moderate - High
Consequences: Slight
Hardware failure
Despite production technology
improving dramatically over the last two decades in relation to
silicon devices, modern computing equipment is cost driven and
generally built down to a price. The result, of course, is equipment
that demonstrates questionable reliability. Hardware failure is
always a major concern. My home computer system is fully redundant
and all data is regularly backed up. Data loss is unlikely.
The
Ti 6000 board can be damaged by improper handling and connection.
Each board costs around $300 , a cost the university is unlikely to
wear in case of failure. Failure of the Ti development board will
inhibit the implementation component of the project.
Risk Factor: Low - Moderate
Consequences: Major Inconvenience Only.
Personal Tragedy
Interruptions to one's life such as
a death in the family or unexpected illness can severely affect a
persons work for a considerable time. No one has to power to
predict such occurrences, all one can do is to assess the risk by
statistical means and develop a strategy if the situation does
occur. In essence the contract between the university and the
student may be up help if delivery was held up due to unforeseen and
uncontrollable circumstance.
Risk Factor: Very Low
Consequences: Moderate – May not affect contract..
From the above analysis the severity and probability of the defined risks are tabulated below.
|
|
Insufficient Literature |
Insufficient Support |
Programming too complex |
Product does not meet expectations |
H/W Failure |
Personal Tragedy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Probability % |
15.00% |
50.00% |
10.00% |
50.00% |
1.00% |
2.00% |
|
Severity /10 |
3 |
4 |
7 |
2 |
5 |
2 |
The table below illustrate how I intend treating risks. Whether I accept the risk or treat the risk before the contract submission.
|
Risk Description |
Accept or Mitigate? |
Action/Comment |
|---|---|---|
|
Insufficient Literature |
Mitigate |
Negotiate contract based on availability of literature. |
|
Insufficient Support |
Accept |
Not a show stopper. |
|
Programming too complex |
Mitigate |
Re-negotiate contract after 6th week. |
|
Product does not meet expectations |
Accept |
Unless product is totally useless a functional demonstration that demonstrates 'promise' in the technology should suffice. |
|
H/W Failure |
Accept |
Redundant system with back ups. Fall back to UNI equipment |
|
Personal Tragedy |
Accept |
Low probability. Contract may account for this on reasonable grounds. |
To monitor the progress of the project and determine whether the project has been exposed to any risks, the project time line must be closely monitored and adhered to. If any one milestone is late, it may indicate that the project is in danger and that the is a risk of project failure. A daily Journal will be kept noting progress including any foreseen problems associated with project delivery.
Communication will take effect in the form of emails to my supervisor when I have a question to pose. I will ensure an update email is sent at least every two weeks to keep the supervisor up to date with progress. Face to face meeting may be required for more complex issues, but will only take place in extraordinary circumstance. The attached time line in appendix A highlights milestones of the project when a submission or report is required.
The Literature So far information gathered has been in the form of journals posted on the Web. Much of this is of an abstract nature however, which few passages describing intricate technical details of any mechanism used to decipher speech.
Many Reference Books have been publish which embraces this technology. Below are some of the more applicable volumes which I will endeavor to get for my research.
|
Title |
Author |
Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
|
Emotion Recognition in Human – Computer interaction |
R. Cowie et al |
This book is the reference for many journals on the subject posted on the net. It deals with speech and facial recognition technologies. Available over the net |
|
Recognition of negative emotions from the speech signal |
C.M. Lee, S Narayanan, R. Pieraccini |
This paper reports on methods for automatic classification of spoken utterances based on the emotional state of the speaker. It reports on an application rolled out by Speechworks in the USA. This will be the ideal reference for my research. Available over the net |
|
Emotion in speech:Recognition and application to call centres |
V Pertrushin |
Another applicable journal. Ideal as it deals with the application to which the results of my research will most likely be employed. Available over the net. |
|
Detecting Emotions in Speech . Thesis |
N. Van Rheede Van Oudtshoorn |
An investigative thesis and Literature review dealing with technology and techniques for analysing and detecting emotions in speech. |
|
|
|
|